Spongy moth, (Lymantria dispar dispar, LDD; formerly gypsy moth) caterpillars were responsible for the largest disturbance to Vermont forests as mapped through aerial detection surveys in 2021. Defoliation was significant in the Champlain Valley of western Vermont, with 50,945 acres mapped as moderately or severely defoliated.


2021 Defoliation
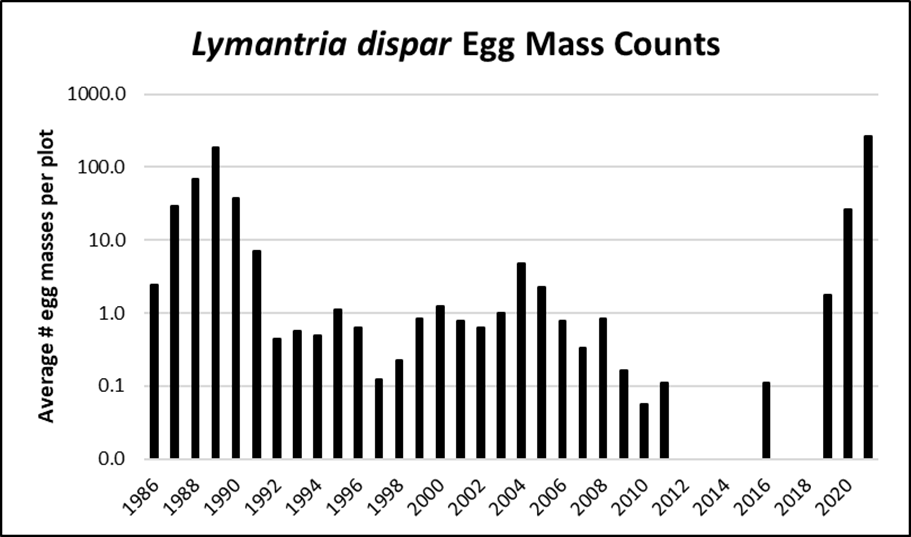
One year of defoliation is unlikely to cause substantial damage to most hardwood trees, but repeated defoliation can have significant impacts on tree and forest health. The fungus Entomophaga maimaiga helps control populations of spongy moth when spring conditions are wet and/or humid. The drought from 2020-2021 may have allowed spongy moth populations to build and expand, and likely contributed to the current outbreak. Outbreaks collapse from a combination of factors: starvation, malnutrition, viral or fungal diseases, and high rates of parasitism.

Egg Mass Counts
More information about spongy moths:
- For identification, biology, and management options, visit VTinvasives.org.
- Spongy moth update - monitoring and management
- WCAX - Experts predict another year of defoliation from the spongy moth
- New York Department of Conservation – Spongy moth
- University of New Hampshire – NH Bugs – Spongy moth
